Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 60mg
Dyspareunia
Estrogen agonist/antagonist indicated for treatment of moderate-to-severe dyspareunia, a symptom of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, due to menopause
60 mg PO qDay with food
Use for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman
Periodically reevaluate to determine if treatment is still necessary
Vaginal Dryness
Indicated for treatment of moderate-to-severe vaginal dryness, a symptom of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, due to menopause
60 mg PO qDay with food
Use for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman
Periodically reevaluate to determine if treatment is still necessary
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment required
Mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment: No dosage adjustment required
Severe hepatic impairment: Not studied; do not use
Safety and efficacy not established
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (9)
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
ospemifene, bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- clomiphene
ospemifene, clomiphene. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- conjugated estrogens
ospemifene, conjugated estrogens. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- dienogest/estradiol valerate
ospemifene, dienogest/estradiol valerate. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- estradiol
ospemifene, estradiol. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
ospemifene, estrogens conjugated synthetic. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- estrogens esterified
ospemifene, estrogens esterified. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- estropipate
ospemifene, estropipate. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
- raloxifene
ospemifene, raloxifene. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated.
Serious - Use Alternative (8)
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP2C19 inducer, with drugs that are CYP2C19 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered.
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered. Adjust dose according to prescribing information if needed. - ceritinib
ceritinib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fexinidazole inhibits CYP3A4. Coadministration may increase risk for adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
- idelalisib
idelalisib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Idelalisib is a strong CYP3A inhibitor; avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates
- ivosidenib
ivosidenib will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with ivosidenib or replace with alternative therapies. If coadministration is unavoidable, monitor patients for loss of therapeutic effect of these drugs.
ivosidenib will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP2C9 substrates with ivosidenib or replace with alternate therapies. If coadministration is unavoidable, monitor patients for loss of therapeutic effect of these drugs. - lonafarnib
lonafarnib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Lonafarnib may increase the AUC and peak concentration of CYP2C19 substrates. If coadministration unavoidable, monitor for adverse reactions and reduce the CYP2C19 substrate dose in accordance with its approved product labeling.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of tucatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If unavoidable, reduce CYP3A substrate dose according to product labeling.
- voxelotor
voxelotor will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Voxelotor increases systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. Consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate(s) if unable to avoid.
Monitor Closely (106)
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- acitretin
acitretin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- alpelisib
alpelisib will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of apalutamide, a weak CYP2C9 inducer, with drugs that are CYP2C9 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered.
- armodafinil
armodafinil increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aspirin
aspirin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- atazanavir
atazanavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bosentan
bosentan decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
bosentan decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - bumetanide
bumetanide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- cannabidiol
cannabidiol will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of sensitive CYP2C19 substrates, as clinically appropriate, when coadministered with cannabidiol.
cannabidiol will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by decreasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Cannabidiol may potentially inhibit CYP2C9 activity. Consider reducing the dose when concomitantly using CYP2C9 substrates. - capecitabine
capecitabine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
carbamazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP3A4 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
- chlorthalidone
chlorthalidone, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- cisplatin
cisplatin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clindamycin
clindamycin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conivaptan
conivaptan increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
ospemifene, conjugated estrogens, vaginal. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- dabrafenib
dabrafenib will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- darunavir
darunavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diphenhydramine
diphenhydramine, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- doxycycline
doxycycline, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- efavirenz
efavirenz decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elagolix
elagolix will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elagolix is a weak CYP2C19 inhibitor. Caution with sensitive CYP2C19 substrates.
elagolix decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elagolix is a weak-to-moderate CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor CYP3A substrates if coadministered. Consider increasing CYP3A substrate dose if needed. - elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- encorafenib
encorafenib, ospemifene. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Encorafenib both inhibits and induces CYP3A4 at clinically relevant plasma concentrations. Coadministration of encorafenib with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased toxicity or decreased efficacy of these agents.
- enzalutamide
enzalutamide decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
eslicarbazepine acetate will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - etravirine
etravirine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates as necessary.
- fenoprofen
fenoprofen, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluconazole
fluconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
fluconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - fluorouracil
fluorouracil increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flurbiprofen
flurbiprofen increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluvoxamine
fluvoxamine will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
fosphenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
fosphenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - furosemide
furosemide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- gemfibrozil
gemfibrozil increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
gemfibrozil increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - glipizide
glipizide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- glyburide
glyburide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ibuprofen
ibuprofen increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ibuprofen, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - iloperidone
iloperidone increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Iloperidone is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor and may lead to increased plasma levels of drugs predominantly eliminated by CYP3A4.
- imatinib
imatinib increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- indinavir
indinavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- indomethacin
indomethacin increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
indomethacin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - isoniazid
isoniazid increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
isoniazid increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates in clinical trials. This effect was not observed with istradefylline 20 mg/day. Consider dose reduction of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
- itraconazole
itraconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
ketoconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - larotrectinib
larotrectinib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lenacapavir
lenacapavir will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Lencapavir may increase CYP3A4 substrates initiated within 9 months after last SC dose of lenacapavir, which may increase potential risk of adverse reactions of CYP3A4 substrates.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
levoketoconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - lopinavir
lopinavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
lopinavir decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - lorlatinib
lorlatinib will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor, ospemifene. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. In vitro studies suggest that lumacaftor may induce and ivacaftor may inhibit CYP2C19 substrates. .
lumacaftor/ivacaftor, ospemifene. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. In vitro studies suggest that lumacaftor may induce and ivacaftor may inhibit CYP2C9 substrates. . - marijuana
marijuana, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- meclofenamate
meclofenamate, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- mefenamic acid
mefenamic acid increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
mefenamic acid, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - mifepristone
mifepristone will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mitotane
mitotane decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Mitotane is a strong inducer of cytochrome P-4503A4; monitor when coadministered with CYP3A4 substrates for possible dosage adjustments.
- modafinil
modafinil increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- naproxen
naproxen, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nefazodone
nefazodone increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nevirapine
nevirapine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nicardipine
nicardipine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
nicardipine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - nitisinone
nitisinone will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Nitisinone inhibits CYP2C9. Caution if CYP2C9 substrate coadministered, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index.
- oxcarbazepine
oxcarbazepine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenobarbital decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - phenytoin
phenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenytoin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
phenytoin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - piroxicam
piroxicam increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
piroxicam, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - posaconazole
posaconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- primidone
primidone decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
primidone decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - quinidine
quinidine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ribociclib
ribociclib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifabutin
rifabutin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifampin
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - rifapentine
rifapentine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifapentine decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ritonavir
ritonavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rucaparib
rucaparib will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- saquinavir
saquinavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- secobarbital
secobarbital decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sparsentan
sparsentan will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sparsentan (a CYP2C9 inducer) decreases exposure of CYP2C9 substrates and reduces efficacy related to these substrates.
sparsentan will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sparsentan (a CYP2C19 inducer) decreases exposure of CYP2C19 substrates and reduces efficacy related to these substrates. - spironolactone
spironolactone, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- stiripentol
stiripentol, ospemifene. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP3A4 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of CYP2C19 substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol. - sulfadiazine
sulfadiazine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
sulfamethoxazole, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - sulindac
sulindac, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tacrolimus
tacrolimus, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- tazemetostat
tazemetostat will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tecovirimat
tecovirimat will decrease the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tecovirimat is a weak CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for effectiveness if coadministered.
- ticlopidine
ticlopidine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tipranavir
tipranavir increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolbutamide
tolbutamide increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
tolbutamide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - tolmetin
tolmetin, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- triclabendazole
triclabendazole will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valproic acid
valproic acid, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- vincristine
vincristine, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- vincristine liposomal
vincristine liposomal, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by plasma protein binding competition. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- voriconazole
voriconazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (9)
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- anastrozole
anastrozole will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chloramphenicol
chloramphenicol increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cimetidine
cimetidine increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyclophosphamide
cyclophosphamide will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- danazol
danazol will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- drospirenone
drospirenone will increase the level or effect of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nitazoxanide
nitazoxanide, ospemifene. Either increases levels of the other by Mechanism: plasma protein binding competition. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- omeprazole
omeprazole increases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
Adverse Effects
1-10%
Hot flush (7.5%)
Vaginal discharge (3.8%)
Muscle spasms (3.2%)
Hyperhidrosis (1.6%)
Genital discharge (1.3%)
Postmarketing reports
Hypersensitivity
Angioedema
Rash
Rash, erythematous
Generalized rash
Pruritus
Urticaria
Neoplasms: Benign, malignant and unspecified, endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer
Vascular disorders: Deep vein thrombosis, thrombosis, pulmonary embolism
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Endometrial cancer
- Elicits estrogenic agonistic effects in the endometrium
- Increased risk of endometrial cancer in women with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens (ie, without a progestin to reduce endometrial hyperplasia)
- Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed and random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding
Cardiovascular effects
- Incidence rates of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic stroke were 1.13 and 3.39 per thousand women years, respectively in the ospemifene 60 mg treatment group and 3.15 and 0 with placebo
- Incidence of DVT was 2.26 per thousand women years (2 reported cases) in the ospemifene 60 mg treatment group and 3.15 per thousand women years (1 reported case) with placebo
Contraindications
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia
History of, or active DVT or PE
History of, or active arterial thromboembolic disease (eg, stroke, MI)
Known or suspected pregnancy or women who may become pregnant
Documented hypersensitivity to drug or ingredients
Cautions
Manage risk factors for cardiovascular disorders, arterial vascular disease (eg, hypertension, DM, smoking, hypercholesterolemia, obesity), and/or venous thromboembolism to reduce risk for progression to serious disease
Increased risk of stroke reported in year 1 and persisted; should thromboembolic or hemorrhagic stroke occur or be suspected, therapy should be discontinued immediately
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) reported; if VTE occurs or suspected, discontinue immediately; when possible, discontinue therapy 4-6 weeks before surgery of the type associated with thromboembolism during prolonged periods of immobilization
Increased risk for endometrial hyperplasia (see Black Box Warnings)
Has not been studied in women with breast cancer; do not use with known or suspected breast cancer or history of breast cancer
Do not use with severe hepatic impairment (not studied)
May initiate or increase occurrence of hot flashes in some women
Breast cancer
- The Women Health Initiative (WHI) substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone provided information about breast cancer in estrogen-alone users; in the WHI estrogen-alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, daily CE-alone was not associated with an increased risk of invasive breast cancer
- After a mean follow-up of 5.6 years, the WHI substudy of daily CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) reported an increased risk of invasive breast cancer in women who took daily CE plus MPA compared to placebo
- In the same substudy, invasive breast cancers were larger, were more likely to be node positive, and were diagnosed at a more advanced stage in the CE (0.625 mg) plus MPA (2.5 mg) group compared with placebo group; metastatic disease was rare, with no apparent difference between the two groups; other prognostic factors, such as histologic subtype, grade and hormone receptor status did not differ between the groups
- Observational studies have reported an increased risk of breast cancer with estrogen plus progestin therapy, and a smaller increase in risk for breast cancer with estrogen-alone therapy, after several years of use; one large meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies reported increased risks that were dependent upon duration of use and could last up to >10 years after discontinuation of estrogen plus progestin therapy and estrogen-alone therapy; extension of WHI Trials also demonstrated increased breast cancer risk associated with estrogen plus progestin therapy
- Observational studies also suggest that the risk of breast cancer was greater, and became apparent earlier, with estrogen plus progestin therapy as compared to risk with estrogen-alone therapy; however, these studies have not found significant variation in risk of breast cancer among different estrogen plus progestin combinations, doses, or routes of administration
- The use of estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation
- All women should receive yearly breast examinations by a healthcare provider and perform monthly breast self-examinations; in addition, mammography examinations should be scheduled based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results
Drug interaction overview
- Ospemifene is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2C9; CYP2C19 also contributes to its metabolism; avoid moderate-to-strong inhibitors of these isoenzymes as they may increase risk of adverse effects
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant; if a woman becomes pregnant while taking this drug, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus
Based on animal data, ospemifene is likely to increase risk for adverse outcomes during pregnancy and labor
Adverse findings at maternally toxic doses included embryofetal lethality in rats and rabbits, and neonatal mortality and difficult labor in rats
Reproductive effects observed are consistent with, and are considered to be related to ospemifene’s estrogen receptor activity
Lactation
Unknown if excreted in human breast milk
Do not breastfeed
Animal studies
- Excreted in rat milk and detected at concentrations higher than that in maternal plasma
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Estrogen agonist/antagonist with tissue selective effects; its biological actions are mediated through binding to estrogen receptors resulting in activation of estrogenic pathways in some tissues and blockade in others
Absorption
Peak plasma time: 2 hr (fasted); 2.5 hr (high fat/high calorie meal)
Peak plasma concentration: 533 ng/mL (fasted); 1198 ng/mL (high fat/high calorie meal)
AUC: 4165 ng•h/mL (fasted); 7521 ng•h/mL (high fat/high calorie meal)
Distribution
Protein bound: >99%
Vd: 448 L
Metabolism
Metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19
Elimination
Half-life: 26 hr
Total body clearance: 9.16 L/hr
Excretion: 75% feces, 7% urine
Administration
Oral Administration
Take with food; food increases bioavailability by ~2-3 fold
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osphena oral - | 60 mg tablet | 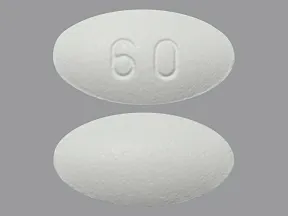 |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
ospemifene oral
OSPEMIFENE - ORAL
(os-PEM-i-feen)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Osphena
WARNING: Ospemifene may increase your risk of uterine cancer. Tell your doctor right away if you develop changes in menstrual period, unusual vaginal bleeding/discharge, or pain/pressure below your "belly button" (navel).Ospemifene may rarely cause serious blood clots to form in the legs or lungs. Tell your doctor if you have a history of blood clots (such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism). Also talk to your doctor about risk factors for developing strokes (sometimes fatal) while taking this medication. Some risk factors include tobacco use, alcohol use, having high cholesterol/diabetes, or a history of heart disease. Talk to your doctor about these risks and the benefits of using ospemifene.
USES: This medication is used to treat painful sexual intercourse and vaginal dryness in women after menopause. Painful intercourse and vaginal dryness are symptoms of changes in and around your vagina, due to menopause.This drug is different from hormones (including estrogens and progestins). It works by acting like estrogen in some parts of the body. Ospemifene belongs to a class of drugs known as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERM).
HOW TO USE: Read the Patient Information Leaflet if available from your pharmacist before you start taking ospemifene and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth with food as directed by your doctor, usually once daily.Use this medication regularly to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, take it at the same time each day.Since this drug can be absorbed through the skin and lungs and may harm an unborn baby, women who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should not handle this medication or breathe the dust from the tablets.Tell your doctor if your condition does not improve or if it worsens.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning section.Hot flashes, vaginal discharge, muscle spasms, and sweating may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.This medication may rarely cause blood clots (such as pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack, deep vein thrombosis). You may be at increased risk for blood clots if you are severely dehydrated, or have a history of blood clots, heart/blood vessel disease, heart failure, stroke, or if you are immobile (such as on very long plane flights or being bedridden). Before using this medication, if you have any of these conditions report them to your doctor or pharmacist. Get medical help right away if any of these side effects occur: shortness of breath/rapid breathing, chest/jaw/left arm pain, unusual sweating, confusion, sudden dizziness/fainting, pain/swelling/warmth in the groin/calf, sudden/severe headaches, trouble speaking, weakness on one side of the body, sudden vision changes.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: See also Warning and Side Effects sections.Before taking ospemifene, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: unusual vaginal bleeding, active or past history of blood clots (such as deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism), active or past history of heart/blood vessel disease (such as heart attack, stroke), cancer, liver disease.Tell your doctor if you just had or will be having surgery or if you will be confined to a bed or chair for a long time (such as a long plane flight). These conditions increase your risk of getting blood clots. You may need to stop this medication for a time or take special precautions.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).This medication must not be used during pregnancy. It may harm an unborn baby. If you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant, tell your doctor right away.Since this drug can be absorbed through the skin and lungs and may harm an unborn baby, women who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should not handle this medication or breathe the dust from the tablets.It is unknown if this medication passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: estrogens, tibolone.Other medications can affect the removal of ospemifene from your body, which may affect how ospemifene works. Examples include fluconazole, rifampin, among others.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.You should have a complete physical examination, breast and pelvic examination, and PAP test (for vaginal cancer) as directed by your doctor, usually at least once a year. You should also have periodic mammograms as determined by your doctor. Follow your doctor's instructions for examining your own breasts. Report any unusual vaginal bleeding, breast pain, or lumps right away. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.



