Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet (Revatio)
- 20mg
tablet (Viagra)
- 25mg
- 50mg
- 100mg
injectable solution (Revatio)
- 10mg/12.5mL
powder for oral suspension (Revatio)
- 10mg/mL (when reconstituted)
oral suspension (Liqrev)
- 10mg/mL
Erectile Dysfunction
Viagra only
Indicated for erectile dysfunction
50 mg PO ~1 hr before sexual activity; however, may be taken anywhere from 30 min to 4 hr before sexual activity
Maximum dosing frequency is once per day
Based on effectiveness and toleration, may increase dose to maximum of 100 mg or decrease to 25 mg
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Revatio, Liqrev only
Indicated for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (World Health Organization [WHO] Group I) to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening
Revatio (PO), Liqrev: 20 mg PO TID; may titrate up to 80 mg TID, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability
Revatio (IV): 10 mg IV bolus TID
10-mg IV predicted to provide pharmacologic effect equivalent to 10-mg oral dose
Do not exceed recommended PO/IV dose
Dosage Modifications
Hepatic impairment
-
Viagra
- Severe (eg, cirrhosis): Consider initial dose of 25 mg
-
Revatio, Liqrev
- Mild or moderate (Child-Pugh A or B): No dose adjustment required
- Severe (Child-Pugh C): Not studied
Renal impairment
-
Viagra
- Mild or moderate (CrCl 30-80 mL/min): No dose adjustment required
- Severe (CrCl <30 mL/min): Consider initial dose of 25 mg
-
Revatio, Liqrev
- Any severity, including severe (CrCl <30 mL/min): No dose adjustment required
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Revatio only
Indicated in children aged 1-17 years for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group I) to improve exercise ability and, in pediatric patients too young to perform standard exercise testing, pulmonary hemodynamics thought to underly improvements in exercise
<20 kg: 10 mg PO TID
20-45 kg: 20 mg PO TID
≥45 kg
- 20 mg PO TID
- Maximum dose in pediatric patients not identified
- Based on experience in adults, dose may be titrated up to 40 mg TID, if required, based on symptoms and tolerability
Dosage Modifications
Hepatic impairment (Revatio)
- Mild or moderate (Child-Pugh A or B): No dose adjustment required
- Severe (Child-Pugh C): Not studied
Renal impairment (Revatio)
- Any severity, including severe (CrCl <30 mL/min): No dose adjustment required
Erectile Dysfunction
Viagra only
Indicated for erectile dysfunction
≥65 years: 25 mg PO initially ~1 hr before sexual activity; however, may be taken anywhere from 30 min to 4 hr before sexual activity
Maximum dosing frequency is once per day
Based on effectiveness and toleration, may increase dose to maximum of 100 mg or decrease to 25 mg
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Revatio only
Indicated for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (World Health Organization [WHO] Group I) to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening
PO: 20 mg PO TID; may titrate up to 80 mg TID, if required , based on symptoms and tolerability
IV: 10 mg IV bolus TID
10-mg IV predicted to provide pharmacologic effect equivalent to 10-mg oral dose
Recommended PO/IV dose not to be exceeded
Adding Revatio to bosentan does not have any beneficial effect on exercise capacity
Clinical trials found no significant difference in response between elderly patients and younger adults; however, cautious dose selection should be considered in elderly because of greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, and cardiac function, as well as comorbid conditions and concomitant pharmacotherapy
Compared with healthy younger volunteers, healthy elderly volunteers (≥65 years) had reduced clearance of sildenafil, resulting in approximately 84% and 107% higher plasma concentrations of sildenafil and its active N-desmethyl metabolite, respectively
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (17)
- atazanavir
atazanavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Never use combination with chronic sildenafil for PAH
- cobicistat
cobicistat will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. When used chronically for PAH, sildenafil is contraindicated for use with cobicistat; if used for erectile dysfunction, do not exceed sildenafil 25 mg q48hr
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Cobicistat is a CYP3A4 inhibitor; contraindicated with CYP3A4 substrates for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events; contraindication applies to chronic administration of sildenafil for PAH; for ED, not to exceed 25 mg in 48 hr.
- isosorbide dinitrate
isosorbide dinitrate, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- isosorbide mononitrate
isosorbide mononitrate, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- nirmatrelvir
nirmatrelvir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening reactions.
- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
nirmatrelvir/ritonavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration contraindicated if sildenafil used for pulmonary arterical hypertension. Reduce sildenafil dose if used for erectile dysfunction.
- nitroglycerin IV
nitroglycerin IV, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nitroglycerin PO
nitroglycerin PO, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nitroglycerin rectal
sildenafil increases effects of nitroglycerin rectal by additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Use of nitroglycerin within a few days of PDE5 inhibitors is contraindicated. PDE5 inhibitors have been shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates.
- nitroglycerin sublingual
nitroglycerin sublingual, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nitroglycerin topical
nitroglycerin topical, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nitroglycerin transdermal
nitroglycerin transdermal, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- nitroglycerin translingual
nitroglycerin translingual, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- riociguat
sildenafil, riociguat. Either increases effects of the other by additive vasodilation. Contraindicated. Coadministration of PDE-5 inhibitors (eg, avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil) and guanylate cyclase stimulators (eg, riociguat) is contraindicated due to risk of additive hypotension; do not administer within 24 hr of each other.
- vericiguat
sildenafil, vericiguat. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of vericiguat with PDE-5 inhibitors may result in additive hypotensive effects.
Serious - Use Alternative (38)
- alfuzosin
sildenafil increases effects of alfuzosin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- amyl nitrite
amyl nitrite, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of apalutamide, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, with drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates can result in lower exposure to these medications. Avoid or substitute another drug for these medications when possible. Evaluate for loss of therapeutic effect if medication must be coadministered. Adjust dose according to prescribing information if needed.
- asenapine
sildenafil increases effects of asenapine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- ceritinib
ceritinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- chloramphenicol
chloramphenicol will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clarithromycin
clarithromycin will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of these phosphodiesterase inhibitors with clarithromycin, a CYP3A4 inhibitor is not recommended. Increased systemic exposure of these drugs may occur with clarithromycin; consider reduction of dosage for phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
- conivaptan
conivaptan will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Delay initiation of treatment with any CYP3A4 substrates for at least 7 days following discontinuation of conivaptan.
- crizotinib
crizotinib increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce crizotnib to 250 mg PO qDay. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, resume crizotinib dose used prior to initiating the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- dabrafenib
dabrafenib will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- doxazosin
sildenafil increases effects of doxazosin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- eslicarbazepine acetate
eslicarbazepine acetate will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- fexinidazole
fexinidazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Fexinidazole inhibits CYP3A4. Coadministration may increase risk for adverse effects of CYP3A4 substrates.
- glyceryl trinitrate pr
glyceryl trinitrate pr, sildenafil. Mechanism: additive vasodilation. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potentially fatal hypotension.
- ivosidenib
ivosidenib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with ivosidenib or replace with alternative therapies. If coadministration is unavoidable, monitor patients for loss of therapeutic effect of these drugs.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and sildenafil (for pulmonary arterial hypertension) is not recommended. When used for erectile dysfunction, consider reducing initial sildenafil dose of 25 mg in patients also taking a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and monitor for sildenafil toxicities (eg, dyspepsia, headache, hypotension).
- lenacapavir
lenacapavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Refer to the prescribing information of PDE5 inhibitors for dose recommendations.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and sildenafil (for pulmonary arterial hypertension) is not recommended. When used for erectile dysfunction, consider reducing initial sildenafil dose of 25 mg in patients also taking a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and monitor for sildenafil toxicities (eg, dyspepsia, headache, hypotension).
- lonafarnib
lonafarnib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A substrates. If coadministration unavoidable, monitor for adverse reactions and reduce CYP3A substrate dose in accordance with product labeling.
- lopinavir
lopinavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mifepristone
mifepristone will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mitotane
mitotane decreases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels.
- nafcillin
nafcillin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If used concomitantly, monitor for toxicities. Patients receiving indinavir with ritonavir should receive not more than 25 mg of sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in a 48-hour period, and patients receiving other protease inhibitors should use a lower initial sildenafil dose of 25 mg. Patient taking sildenafil for PAH with ritonavir is not recommended.
- oxcarbazepine
oxcarbazepine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- pentobarbital
pentobarbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- phenoxybenzamine
sildenafil increases effects of phenoxybenzamine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- phentolamine
sildenafil increases effects of phentolamine by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- phenytoin
phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- prazosin
sildenafil increases effects of prazosin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- primidone
primidone will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- ritonavir
ritonavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If used concomitantly, monitor for toxicities. Patients receiving indinavir with ritonavir should receive not more than 25 mg of sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in a 48-hour period, and patients receiving other protease inhibitors should use a lower initial sildenafil dose of 25 mg. Patient taking sildenafil for PAH with ritonavir is not recommended.
- silodosin
sildenafil increases effects of silodosin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- St John's Wort
St John's Wort will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- terazosin
sildenafil increases effects of terazosin by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Risk of hypotension; separate sildenafil >25mg from alpha blocker by 4hr.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of tucatinib with CYP3A substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If unavoidable, reduce CYP3A substrate dose according to product labeling.
- voxelotor
voxelotor will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Voxelotor increases systemic exposure of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index. Consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate(s) if unable to avoid.
Monitor Closely (88)
- acebutolol
acebutolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- amifostine
amifostine increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- amobarbital
amobarbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- aprepitant
aprepitant will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- armodafinil
armodafinil will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- artemether/lumefantrine
artemether/lumefantrine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atenolol
atenolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- benazepril
sildenafil, benazepril. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Enhanced hypotensive effects.
- betaxolol
betaxolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- bisoprolol
bisoprolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- bosentan
bosentan will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- butabarbital
butabarbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butalbital
butalbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- captopril
sildenafil, captopril. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Both drugs lower blood pressure. Monitor blood pressure.
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- carvedilol
carvedilol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP3A4 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
- cimetidine
cimetidine will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cyclosporine
cyclosporine will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- danazol
danazol will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- darunavir
darunavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with PDE-5 inhibitors may result in an increase in PDE-5 inhibitor-associated adverse reactions (eg, hypotension, syncope, visual disturbances and priapism).
- deferasirox
deferasirox will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexamethasone
dexamethasone will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- diltiazem
diltiazem will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dronedarone
dronedarone will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- duvelisib
duvelisib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with duvelisib increases AUC of a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate which may increase the risk of toxicities of these drugs. Consider reducing the dose of the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate and monitor for signs of toxicities of the coadministered sensitive CYP3A substrate.
- efavirenz
efavirenz will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- elagolix
elagolix decreases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Elagolix is a weak-to-moderate CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor CYP3A substrates if coadministered. Consider increasing CYP3A substrate dose if needed.
- encorafenib
encorafenib, sildenafil. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Encorafenib both inhibits and induces CYP3A4 at clinically relevant plasma concentrations. Coadministration of encorafenib with sensitive CYP3A4 substrates may result in increased toxicity or decreased efficacy of these agents.
- enzalutamide
enzalutamide will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- epoprostenol
epoprostenol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- erythromycin base
erythromycin base will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a starting dose of 25 mg in patients treated with erythromycin.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
erythromycin ethylsuccinate will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a starting dose of 25 mg in patients treated with erythromycin.
- erythromycin lactobionate
erythromycin lactobionate will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a starting dose of 25 mg in patients treated with erythromycin.
- erythromycin stearate
erythromycin stearate will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a starting dose of 25 mg in patients treated with erythromycin.
- esmolol
esmolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- etravirine
etravirine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- fedratinib
fedratinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Adjust dose of drugs that are CYP3A4 substrates as necessary.
- fluconazole
fluconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- fosaprepitant
fosaprepitant will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosphenytoin
fosphenytoin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- grapefruit
grapefruit will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- griseofulvin
griseofulvin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydrocortisone
hydrocortisone will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- idelalisib
idelalisib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of sildenafil with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is not recommended. If using Viagra, consider decreasing starting dose.
- iloperidone
iloperidone increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Iloperidone is a time-dependent CYP3A inhibitor and may lead to increased plasma levels of drugs predominantly eliminated by CYP3A4.
- indinavir
indinavir will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. If used concomitantly, monitor for toxicities. Patients receiving indinavir with ritonavir should receive not more than 25 mg of sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in a 48-hour period, and patients receiving other protease inhibitors should use a lower initial sildenafil dose of 25 mg.
- isoniazid
isoniazid will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of CYP3A4 substrates in clinical trials. This effect was not observed with istradefylline 20 mg/day. Consider dose reduction of sensitive CYP3A4 substrates.
- itraconazole
itraconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Not recommended during and 2 weeks after itraconazole treatment when sildenafil is used for pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- labetalol
labetalol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- lapatinib
lapatinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lesinurad (DSC)
lesinurad (DSC) decreases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- letermovir
letermovir increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levamlodipine
levamlodipine, sildenafil. anti-hypertensive channel blocking. Use Caution/Monitor. When amlodipine and sildenafil were used in combination, each agent independently exerted its own blood pressure lowering effect.
- lorlatinib
lorlatinib will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- maraviroc
maraviroc, sildenafil. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Increased risk of orthostatic hypotension.
- mavacamten
sildenafil will increase the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Inititiation of weak CYP2C19 inhibitors may require decreased mavacamten dose.
- metoprolol
metoprolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- miconazole vaginal
miconazole vaginal will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nebivolol
nebivolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- nefazodone
nefazodone will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nevirapine
nevirapine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- nifedipine
nifedipine will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nilotinib
nilotinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nitroprusside sodium
nitroprusside sodium, sildenafil. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Additive hypotensive effects.
- penbutolol
penbutolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- pindolol
pindolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- posaconazole
posaconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- propranolol
propranolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- ribociclib
ribociclib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rifabutin
rifabutin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- rifampin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- rifapentine
rifapentine will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- saquinavir
saquinavir increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. Increased risk of priapism, hypotension, and other adverse effects.
- secobarbital
secobarbital will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sotalol
sotalol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- stiripentol
stiripentol, sildenafil. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP3A4 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP3A4 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP3A4 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
- tamsulosin
sildenafil, tamsulosin. Either increases effects of the other by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Risk of hypotension.
- tazemetostat
tazemetostat will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tecovirimat
tecovirimat will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Tecovirimat is a weak CYP3A4 inducer. Monitor sensitive CYP3A4 substrates for effectiveness if coadministered.
- timolol
timolol increases effects of sildenafil by additive vasodilation. Use Caution/Monitor. Sildenafil has systemic vasodilatory properties and may further lower blood pressure in patients taking antihypertensive medications. Monitor blood pressure response to sildenafil in patients receiving concurrent blood pressure lowering therapy.
- tipranavir
tipranavir increases levels of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potential for increased toxicity. Increased risk of priapism, hypotension, and other adverse effects.
- tobramycin inhaled
tobramycin inhaled and sildenafil both increase nephrotoxicity and/or ototoxicity. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concurrent or sequential use to decrease risk for ototoxicity
- verapamil
verapamil will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- voriconazole
voriconazole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zafirlukast
zafirlukast will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (8)
- acetazolamide
acetazolamide will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- anastrozole
anastrozole will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cyclophosphamide
cyclophosphamide will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- drospirenone
drospirenone will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- labetalol
sildenafil increases effects of labetalol by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Risk of hypotension.
- larotrectinib
larotrectinib will increase the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- macitentan
macitentan increases levels of sildenafil by unspecified interaction mechanism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Systemic exposure of steady-state sildenafil (20 mg TID) increased by 15% during coadministration of macitentan (10 mg/day); this change is not considered clinically relevant.
- sapropterin
sapropterin, sildenafil. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Possible additive vasorelaxation, leading to low blood pressure.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Viagra
-
25-mg dose
- Headache (16%)
-
50-mg dose
- Headache (21%)
- Flushing (19%)
- 100-mg dose H5
- Headache (28%)
- Flushing (18%)
- Dyspepsia (17%)
- Abnormal vision (11%)
Revatio
- Headache (46%)
- Dyspepsia (13%)
1-10%
Viagra
-
25-mg dose
- Flushing (10%)
- Nasal congestion (4%)
- Dyspepsia (3%)
- Back pain (3%)
- Dizziness (3%)
- Myalgia (2%)
- Nausea (2%)
- Abnormal vision (1%)
- Rash (1%)
-
50-mg dose
- Dyspepsia (9%)
- Nasal congestion (4%)
- Back pain (4%)
- Dizziness (4%)
- Nausea (3%)
- Abnormal vision (2%)
- Myalgia (2%)
- Rash (2%)
-
100-mg dose
- Nasal congestion (9%)
- Back pain (4%)
- Myalgia (4%)
- Nausea (3%)
- Dizziness (3%)
- Rash (3%)
-
<2% with potential causal relationship
- Body as a whole: Face edema, photosensitivity reaction, shock, asthenia, pain, chills, accidental fall, abdominal pain, allergic reaction, chest pain, accidental injury
- Cardiovascular: Angina pectoris, AV block, migraine, syncope, tachycardia, palpitation, hypotension, postural hypotension, myocardial ischemia, cerebral thrombosis, cardiac arrest, heart failure, abnormal electrocardiogram, cardiomyopathy
- Digestive: Vomiting, glossitis, colitis, dysphagia, gastritis, gastroenteritis, esophagitis, stomatitis, dry mouth, liver function tests abnormal, rectal hemorrhage, gingivitis
- Hemic and lymphatic: Anemia and leukopenia
- Metabolic and nutritional: Thirst, edema, gout, unstable diabetes, hyperglycemia, peripheral edema, hyperuricemia, hypoglycemic reaction, hypernatremia
- Musculoskeletal: Arthritis, arthrosis, myalgia, tendon rupture, tenosynovitis, bone pain, myasthenia, synovitis
- Nervous: Ataxia, hypertonia, neuralgia, neuropathy, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo, depression, insomnia, somnolence, abnormal dreams, reflexes decreased, hypesthesia
- Respiratory: Asthma, dyspnea, laryngitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, sputum increased, cough increased
- Skin and appendages: Urticaria, herpes simplex, pruritus, sweating, skin ulcer, contact dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis
- Special senses: Sudden decrease or loss of hearing, mydriasis, conjunctivitis, photophobia, tinnitus, eye pain, ear pain, eye hemorrhage, cataract, dry eyes
- Urogenital: Cystitis, nocturia, urinary frequency, breast enlargement, urinary incontinence, abnormal ejaculation, genital edema and anorgasmia
Revatio
- Flushing (10%)
- Epistaxis (9%)
- Diarrhea (9%)
- Insomnia (7%)
- Myalgia (7%)
- Dyspnea exacerbate (7%)
- Erythema (6%)
- Pyrexia (6%)
- Rhinitis (4%)
- Gastritis (3%)
- Sinusitis (3%)
- Paresthesia (3%)
Postmarketing Reports
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular: Serious cardiovascular (CV), cerebrovascular, and vascular events, including myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death, ventricular arrhythmia, cerebrovascular hemorrhage, transient ischemic attack, hypertension, subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhages, and pulmonary hemorrhage (most, but not all, of these patients had preexisting CV risk factors)
Hemic and lymphatic: vaso-occlusive crisis: In a small, prematurely terminated study of sildenafil in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) secondary to sickle cell disease, vaso-occlusive crises requiring hospitalization were commonly reported
Nervous: Seizure, seizure recurrence, anxiety, and transient global amnesia
Respiratory: Epistaxis
Hearing: Cases of sudden decrease or loss of hearing reported postmarketing in temporal association with PDE5 inhibitors
Ocular: Diplopia, temporary vision loss/decreased vision, ocular redness or bloodshot appearance, ocular burning, ocular swelling/pressure, increased intraocular pressure, retinal edema, retinal vascular disease or bleeding, and vitreous traction/detachment
Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a cause of decreased vision including permanent loss of vision (reported rarely)
Urogenital: Prolonged erection, priapism, and hematuria
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators (eg, riociguat); concomitant use can cause hypotension
Coadministration with nitrates
- Coadministration with nitrates (either regularly and/or intermittently) and nitric oxide donors
- Consistent with the effects of PDE5 inhibition on the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway, PDE5 inhibitors may potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates
- A suitable time interval following PDE5 dosing for the safe administration of nitrates or nitric oxide donors has not been determined
Cautions
Elicits vasodilatory properties, resulting in mild and transient decreases in blood pressure; monitor for hypotension
Use with caution in patients with anatomic deformation of penis (eg, angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie disease), conditions potentially predisposing to priapism (eg, sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia), cardiovascular disease, bleeding disorders, active peptic ulcer disease, liver disease, renal impairment, multidrug antihypertensive regimens, retinitis pigmentosa, concomitant use of CYP3A4 inhibitors
Pulmonary vasodilators may significantly worsen cardiovascular status of patients with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease
Sudden decrease or loss of hearing, which may be accompanied by tinnitus and dizziness
Stop sildenafil and seek medical care if a sudden loss of vision occurs in 1 or both eyes, which could be a sign of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION); use with caution, and only when the anticipated benefits outweigh the risks, most patients had underlying anatomic or vascular risk factors for developing NAION, including low cup to disc ratio (“crowded disc”); advise patients to seek immediate medical attention in the event of a sudden loss of vision
May cause dose-related impairment of color discrimination; use in patients with retinitis pigmentosa not recommended
Viagra
- Potential for cardiac risk with sexual activity in patients with preexisting cardiovascular disease; therefore, treatment for erectile dysfunction generally should not be instituted in men for whom sexual activity is inadvisable because of their underlying cardiovascular status
- Evaluate underlying causes of erectile dysfunction or BPH before initiating therapy
Revatio
- In small, prematurely terminated study of patients with PAH secondary to sickle-cell disease, vaso-occlusive crises requiring hospitalization were more commonly reported by patients who received sildenafil than by those randomized to placebo; effectiveness of sildenafil in PAH secondary to sickle-cell anemia has not been established; the clinical relevance to men treated for erectile dysfunction with sildenafil is not known
- Epistaxis occurred in 13% of patients with PAH secondary to connective tissue disease (eg, scleroderma); this effect was not seen in idiopathic PAH; incidence was also higher in those receiving concomitant PO vitamin K antagonist therapy (9%) than in those not receiving such therapy (2%)
Drug interaction overview
- CYP3A substrate (major route); CYP2C9 substrate (minor route)
-
Nitrates
- Contraindicated
- Consistent with its known effects on the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway, sildenafil was shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of nitrates
-
Strong CYP3A inhibitors
- Viagra: Modify dose; not to exceed single dose of 25 mg/48 hr
- Revatio: Not recommended
- Coadministration increases systemic exposure of sildenafil and risk of adverse effects
-
Moderate-to-strong CYP3A inducers
- Revatio: Modify dose; upward dose titration may be needed if coadministered
- Coadministration with moderate-to-strong CYP3A inducers (eg, bosentan) decreases the sildenafil exposure and possibly reduces efficacy
-
Other PDE5 inhibitors
- Avoid
- Additive adverse effects may occur if coadministered with other PDE5 inhibitors (eg, avanafil, tadalafil, vardenafil)
-
Alpha-blockers or antihypertensives
- Modify dose/caution
- Coadministration may increase risk of hypotension
- Particularly with higher doses used for erectile dysfunction
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Limited published data from randomized controlled trials, case-controlled trials, and case series do not report a clear association with sildenafil and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when sildenafil is used during pregnancy; there are risks to mother and fetus from untreated pulmonary arterial hypertension
Pregnant women with untreated pulmonary arterial hypertension are at risk for heart failure, stroke, preterm delivery, and maternal and fetal death
Lactation
Limited published data from a case report describe presence of sildenafil and its active metabolite in human milk; there is insufficient information about effects of sildenafil on breastfed infant and no information on effects of sildenafil on milk production; limited clinical data during lactation preclude a clear determination of risk of drug to an infant during lactation
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits PDE-5, increasing cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP to allow smooth-muscle relaxation
Absorption
Bioavailability: 40%
Peak plasma time: 30-120 min
Metabolism
Metabolized in liver by CYP3A4 and (in minor amounts) CYP2C9
Metabolites: N-desmethyl metabolite (active; possesses 50% of sildenafil's PDE-5-inhibiting activity)
Elimination
Half-life: Parent drug, 3-4 hr; active metabolite, 10-70 min
Excretion: Feces (80%), urine (13%)
Administration
IV Administration
Revatio: Administer as an IV bolus
Oral Administration
Viagra
- May take with or without food
- Take as needed, about 1 hr before sexual activity; however, may be taken anywhere from 30 minutes to 4 hr before sexual activity
- The maximum recommended dosing frequency is once daily
Revatio
- May take with or without food
-
Reconstitution of oral suspension
- Reconstitute bottle contents with water (total volume of 90 mL [60 mL followed by 30 mL])
- Refer to prescribing information for detailed instructions
- Do not mix with any other medication or additional flavoring agent
Storage
Revatio tablets or IV solution
- Store at controlled room temperature 20-25°C (68-77°F)
- Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F)
Revatio reconstituted oral suspension
- Store <30°C (86°F) or in a refrigerator between 2-8°C (36-46°F)
- Do not freeze
- Discard unused oral suspension after 60 days
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viagra oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| Viagra oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| Viagra oral - | 25 mg tablet | 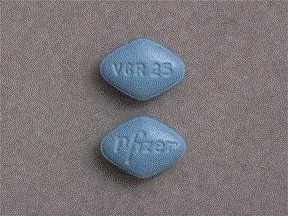 | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet | 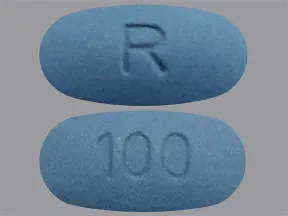 | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet | 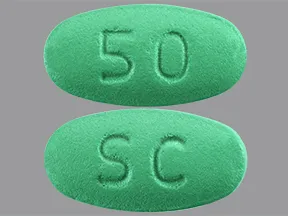 | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 100 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 50 mg tablet |  | |
| sildenafil oral - | 25 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
sildenafil oral
SILDENAFIL - ORAL
(sil-DEN-a-fil)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Viagra
USES: Sildenafil is used to treat male sexual function problems (impotence or erectile dysfunction-ED). In combination with sexual stimulation, sildenafil works by increasing blood flow to the penis to help a man get and keep an erection.This drug does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (such as HIV, hepatitis B, gonorrhea, syphilis). Practice "safe sex" such as using latex condoms. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
HOW TO USE: Read the Patient Information Leaflet if available from your pharmacist before you start taking sildenafil and each time you get a refill. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.To treat erectile dysfunction-ED, take this drug by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually as needed. Take sildenafil at least 30 minutes, but no more than 4 hours, before sexual activity (1 hour before is the most effective). Do not take more than once daily.A high-fat meal may delay how quickly the drug begins to work.The dosage is based on your medical condition, response to treatment, and other medications you may be taking. Be sure to tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Tell your doctor if your condition does not improve.
SIDE EFFECTS: Dizziness, headache, flushing, or stomach upset may occur. Vision changes such as increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or trouble telling blue and green colors apart may also occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.To reduce the risk of dizziness and lightheadedness, get up slowly when rising from a sitting or lying position.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Sexual activity may put extra strain on your heart, especially if you have heart problems. If you have heart problems and experience any of these serious side effects while having sex, stop and get medical help right away: severe dizziness, fainting, chest/jaw/left arm pain, nausea.Rarely, sudden decreased vision, including permanent blindness, in one or both eyes (NAION) may occur. If this serious problem occurs, stop taking sildenafil and get medical help right away. You have a slightly greater chance of developing NAION if you have heart disease, diabetes, high cholesterol, certain other eye problems ("crowded disk"), high blood pressure, if you are over 50, or if you smoke.Rarely, a sudden decrease or loss of hearing, sometimes with ringing in the ears and dizziness, may occur. Stop taking sildenafil and get medical help right away if these effects occur.In the rare event you have a painful or prolonged erection lasting 4 or more hours, stop using this drug and get medical help right away, or permanent problems could occur.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking sildenafil, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: heart problems (such as heart attack or life-threatening irregular heartbeat in the past 6 months, chest pain/angina, heart failure), stroke in the past 6 months, kidney disease, liver disease, high or low blood pressure, dehydration, penis conditions (such as angulation, fibrosis/scarring, Peyronie's disease), history of painful/prolonged erection (priapism), conditions that may increase the risk of priapism (such as sickle cell anemia, leukemia, multiple myeloma), eye problems (such as retinitis pigmentosa, sudden decreased vision, NAION).This drug may make you dizzy or cause vision problems. Alcohol or marijuana (cannabis) can make you more dizzy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do anything that needs alertness or clear vision until you can do it safely. Limit alcoholic beverages. Talk to your doctor if you are using marijuana (cannabis).Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).During pregnancy, sildenafil should be used only when clearly needed. Since high blood pressure in the lungs is a serious condition that can harm both a pregnant woman and her unborn baby, do not stop this medication unless directed by your doctor. If you are planning pregnancy, become pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of using sildenafil.This medication passes into breast milk in small amounts. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug are: riociguat, vericiguat.Sildenafil can cause a serious drop in your blood pressure when used with nitrates. A serious drop in blood pressure can lead to dizziness, fainting, and rarely heart attack or stroke. Do not use sildenafil with any of the following: certain drugs used to treat chest pain/angina (nitrates such as nitroglycerin, isosorbide), recreational drugs called "poppers" containing amyl nitrate, amyl nitrite, or butyl nitrite.If you are also taking an alpha blocker medication (such as doxazosin, tamsulosin) to treat an enlarged prostate/BPH or high blood pressure, your blood pressure may get too low which can lead to dizziness or fainting. Your doctor may start treatment with a lower dose of sildenafil to minimize your risk of low blood pressure.Other medications can affect the removal of sildenafil from your body, which may affect how sildenafil works. Examples include azole antifungals (such as itraconazole, ketoconazole), macrolide antibiotics (such as clarithromycin, erythromycin), HIV protease inhibitors (such as saquinavir), mifepristone, rifampin, ritonavir, among others.Do not take this medication with any other product that contains sildenafil or other similar medications for erectile dysfunction-ED or pulmonary hypertension (such as tadalafil, vardenafil).
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include severe dizziness, fainting, painful/prolonged erection.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.
MISSED DOSE: Not applicable.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised March 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.